Industrial liquid ammonia

Specifications
| Item | Index | |||
| First class product | Quality product | |||
| Appearance | Colorless, irritating and smelly liquefied gas | |||
| Ammonia content,% ≥ | 99.6 | 99.0 | ||
| Residue content,% ≤ | 0.4 | Measured | ||
| Moisture,%≤ | 0.10 | Measured | ||
| Iron content, mg/kg ≤ | 1 | — | ||
| Hydrogen sulfide content, mg/kg ≤ | 1.0 | 5 | ||
Packing & Storage
| Packing | Steel gas cylinders. | |||||||
| Storage | Store in a cool and ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 30℃. It should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, halogens, and edible chemicals, and should not be mixed. Explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities are adopted. It is forbidden to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency treatment equipment for leakage. | |||||||
| Transportation | The railway transportation time limit of this product is shipped by self-owned tankers of pressure-resistant liquefied petroleum gas enterprises, and it must be reported to the relevant departments for approval before shipment. | |||||||
Free Quote
At present, the company has more than 10 advanced production lines of the hollow glass microspheres with the annual production capacity of 15 thousand tons. To meet the demand of customers, the company can expand production capacity as soon as possible within 20 days. 6S principles Implemented in the production systems.
For samples, pricing, or more information, please call us at 0086 25 51192301 or mail to info@ascent-chem.com or fill out the following form. We will respond to you as soon as possible.
Tel: 0086 25 51192301
E-mail: info@ascent-chem.com


General Information
| Common Names | Industrial liquid ammonia | |||||||
| Structure | 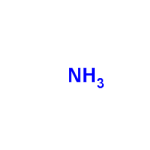 H3N H3N | |||||||
| CAS No. | 7664-41-7 | Boiling Point (℃) | -33.4±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |||||
| Molecular Weight | 17.031 | Melting Point (℃) | −78 °C(lit.) | |||||
| Appearance | Density | 1.023 g/mL at 25 °C | ||||||
| HS Code | 2814100000 | Flash Point | 52 °F | |||||
| Solubility | Soluble in water, ethanol, and ether. | Vapor pressure | 5992.5±0.0 mmHg at 25°C | |||||
| Safety Phrases | S26-S7-S45-S36/37/39-S16-S9-S61 | ||
| RIDADR | UN 1219 3/PG 2 | ||
| WGK Germany | 2 | ||
| Packaging Group | II | ||
| Hazard Class | 3 | ||
| FIRST AID | |
| Inhalation | Don’t delay time and move the victim to fresh air. If the victim cannot return to normal quickly, he or she must be transferred to the nearest medical institution for further treatment. |
| Skin | Take off the contaminated clothing and immediately rinse the contaminated skin with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes, and then wash with soap if possible. If there is redness, swelling, pain, or blisters, transfer to the nearest medical institution for further treatment. |
| Eyes | Immediately rinse your eyes with plenty of water, while keeping your eyelids open, rinse for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical attention nearby. |
| Ingestion | Do not induce vomiting.Immediately take them to the nearest medical facility for further treatment.If spontaneous vomiting occurs, keep your head low and your legs high to prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract. |
Frequently Asked Questions
The role of liquid ammonia
Liquid ammonia, which is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NH3, plays various important roles in different fields. Here are some significant applications and uses of liquid ammonia:
1. Fertilizer Production: Ammonia is a key component in the production of fertilizers. It is used as a raw material for the synthesis of ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulfate, and other nitrogen-based fertilizers. These fertilizers provide essential nutrients to plants, promoting their growth and improving crop yields.
2. Refrigeration and Air Conditioning: Liquid ammonia is used as a refrigerant in industrial refrigeration systems and air conditioning units. It has excellent heat transfer properties and is highly efficient in absorbing and releasing heat, making it suitable for cooling applications.
3. Chemical Manufacturing: Ammonia serves as a building block for the production of various chemicals. It is used in the synthesis of nitric acid, which is further utilized in the manufacture of explosives, dyes, and other chemical compounds. Ammonia is also a precursor in the production of plastics, fibers, pharmaceuticals, and cleaning agents.
4. Cleaning Agent: Ammonia is an effective cleaning agent due to its ability to dissolve greases, oils, and dirt. It is commonly used in household cleaners, glass cleaners, and floor cleaners. However, caution should be exercised when using ammonia as it can be irritating to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system.
5. Water Treatment: Liquid ammonia is used in water treatment processes to remove contaminants. It can be added to water as a disinfectant to kill bacteria and other microorganisms. Additionally, ammonia can be employed in the removal of heavy metals from wastewater through a process called ion exchange.
6. Analytical Chemistry: Ammonia is frequently used in analytical chemistry for various purposes. It can be utilized as a reagent to determine the presence and concentration of various substances in a sample. Ammonia-based reagents are employed in techniques such as titration, spectrophotometry, and gas chromatography.
7. Fuel: Ammonia has gained attention as a potential alternative fuel source. It can be used as a hydrogen carrier, where the ammonia is broken down to release hydrogen for use in fuel cells or combustion engines. This approach allows for the storage and transportation of hydrogen more easily than in its pure form.
It is important to note that while liquid ammonia has many useful applications, it can also be hazardous. Ammonia is toxic and can cause harm to humans and the environment if not handled properly. Safety precautions should always be followed when working with or around liquid ammonia.
Contact Us
TEL: 0086 25 51192301
EMAIL: info@ascent-chem.com
EMAIL: sophiahoney247@gmail.com
Copyright © Ascent Sbr All Rights Reserved.

