Industrial ethylene

Specifications
| Item | Index | |||
| Superior product | First class product | |||
| Ethylene,% (volume fraction) ≥ | 99.95 | 99.90 | ||
| Methane and ethane, (mL/m3) ≤ | 500 | 1000 | ||
| Carbon three and carbon three or more, (mL/m3) ≤ | 20 | 50 | ||
| Carbon monoxide, (mL/m3) ≤ | 2 | 5 | ||
| Carbon dioxide, (mL/m3) ≤ | 5 | 10 | ||
| Hydrogen, (mL/m3) ≤ | 5 | 10 | ||
| Oxygen, (mL/m3) ≤ | 2 | 5 | ||
| Acetylene, (mL/m3) ≤ | 5 | 10 | ||
| Sulfur, (mg/kg) ≤ | 1 | 2 | ||
| Water, (mL/m3) ≤ | 5 | 10 | ||
| Methanol, (mg/kg) ≤ | 10 | |||
Packing & Storage
| Packing | Steel gas cylinders | |||||||
| Storage | Store in a cool and ventilated special warehouse for flammable gases. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 30℃. | |||||||
| Transportation | During transportation, the transportation vehicle should be equipped with corresponding varieties and quantities of fire-fighting equipment.The exhaust pipe of the vehicle in which the item is shipped must be equipped with a fire-proof device, and the use of sparks is prohibited. | |||||||
Free Quote
At present, the company has more than 10 advanced production lines of the hollow glass microspheres with the annual production capacity of 15 thousand tons. To meet the demand of customers, the company can expand production capacity as soon as possible within 20 days. 6S principles Implemented in the production systems.
For samples, pricing, or more information, please call us at 0086 25 51192301 or mail to info@ascent-chem.com or fill out the following form. We will respond to you as soon as possible.
Tel: 0086 25 51192301
E-mail: info@ascent-chem.com


General Information
| Common Names | Industrial ethylene, Ethylene | |||||||
| Structure | 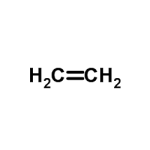 C2H4 C2H4 | |||||||
| CAS No. | 74-85-1 | Boiling Point (℃) | -103.7±7.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |||||
| Molecular Weight | 28.053 | Melting Point (℃) | −169 °C(lit.) | |||||
| Appearance | Colorless gas with a slight odor unique to hydrocarbons. | Density | 0.00126 | |||||
| HS Code | 2901210000 | Flash Point | -125.1±13.0 °C | |||||
| Solubility | It is insoluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, soluble in ether, acetone, and benzene | Vapor pressure | 43302.6±0.1 mmHg at 25°C | |||||
| Safety Phrases | S9-S16-S33-S46 | ||
| RIDADR | UN 1962 2.1 | ||
| WGK Germany | — | ||
| Packaging Group | N/A | ||
| Hazard Class | 2.1 | ||
| FIRST AID | |
| Inhalation | Don’t delay time and move the victim to fresh air. If the victim cannot return to normal quickly, he or she must be transferred to the nearest medical institution for further treatment. |
| Skin | Take off the contaminated clothing and immediately rinse the contaminated skin with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes, and then wash with soap if possible. If there is redness, swelling, pain, or blisters, transfer to the nearest medical institution for further treatment. |
| Eyes | Immediately rinse your eyes with plenty of water, while keeping your eyelids open, rinse for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical attention nearby. |
| Ingestion | Do not induce vomiting.Immediately take them to the nearest medical facility for further treatment.If spontaneous vomiting occurs, keep your head low and your legs high to prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract. |

Frequently Asked Questions
Applications of Industrial ethylene
Industrial ethylene, also known as ethene, is a crucial building block in the petrochemical industry. It is primarily produced through the steam cracking of hydrocarbon feedstocks, such as natural gas, naphtha, and ethane. Ethylene has numerous applications across various industries due to its versatile properties. Some of the key applications of industrial ethylene include:
1. Polyethylene Production: The largest application of ethylene is in the production of polyethylene, a widely used plastic. Polyethylene is utilized in diverse industries, including packaging, construction, automotive, agriculture, and consumer goods.
2. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Production: Ethylene is a key raw material for the production of polyvinyl chloride, a versatile thermoplastic. PVC finds applications in construction, piping systems, electrical insulation, healthcare products, and more.
3. Styrene Production: Ethylene is a starting material for the production of styrene, which is further polymerized to form polystyrene. Polystyrene is used in packaging, insulation, disposable products, and various consumer goods.
4. Ethylene Oxide Production: Ethylene can be oxidized to produce ethylene oxide, which is a vital chemical intermediate. Ethylene oxide is used in the production of surfactants, detergents, solvents, antifreeze, textiles, and pharmaceuticals.
5. Ethylene Glycol Production: Ethylene can be converted to ethylene glycol through a process called hydration. Ethylene glycol is widely used as an antifreeze, coolant, and raw material in the production of polyester fibers, films, and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) resins.
6. Ethylene Dichloride (EDC) Production: Ethylene reacts with chlorine to form ethylene dichloride, which is a precursor to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) production. EDC is also used as a solvent, degreaser, and in the production of other chemicals.
7. Ethyleneamines Production: Ethyleneamines, such as ethylenediamine (EDA), diethylenetriamine (DETA), and triethylenetetramine (TETA), are produced from ethylene. These chemicals find applications in various industries, including agriculture, adhesives, coatings, pharmaceuticals, and fuel additives.
8. Synthetic Rubber Production: Ethylene is a key ingredient in the production of various synthetic rubbers, including polybutadiene, styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), and ethylene-propylene-diene monomer (EPDM). Synthetic rubbers are used in the manufacturing of tires, belts, hoses, seals, and other automotive and industrial applications.
9. Solvents and Chemical Intermediates: Ethylene is used in the production of various solvents, such as ethanol, ethylbenzene, and ethylene dichloride. These solvents have applications in industries such as paints, coatings, adhesives, and cleaning products.
10. Fuel and Energy: Ethylene can be used as a fuel or as a feedstock for the production of other fuels, such as ethane, propylene, and butadiene. Ethylene-based fuels are primarily used in industrial heating and power generation.
These are just some of the many applications of industrial ethylene. Its versatility and wide range of applications make it one of the most important chemicals in the modern petrochemical industry.
Contact Us
TEL: 0086 25 51192301
EMAIL: info@ascent-chem.com
EMAIL: sophiahoney247@gmail.com
Copyright © Ascent Sbr All Rights Reserved.

